Abstract
Background: Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is an indolent B-cell lymphoma with a heterogeneous disease course. For nearly a decade, the International Prognostic Scoring system (IPSS), requiring 5 variables (platelet count, hemoglobin, age, Beta 2 microglobulin and immunoglobulin M size) has been used to prognosticate patients with active WM. In this study, we attempt to propose a simplified prognostic model for patients with active/symptomatic WM.
Methods: All patients with active WM diagnosed between 01/01/1996 and 12/31/2017 and evaluated consecutively at Mayo Clinic, Rochester were included in the study after Institutional Review Board approval. Active WM was defined as ≥10% marrow infiltration with lymphoplasmacytic cells plus monoclonal IgM of any size requiring systemic therapy. The follow up and overall survival (OS) were calculated from the time of active WM until date of last follow up or death. Baseline parameters at active disease were used to assess prognostic factors for OS using a univariate followed by a multivariate (MV) Cox regression analysis. Independent variables on the MV analysis were given a score proportional to their risk ratios (RR). All time-to-event analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and the survival curves were compared using log-rank test. Discriminatory ability of the IPSS and the currently proposed prognostic system was assessed using Harrell's concordance index wherein a higher c-statistic is associated with a better discriminatory ability.
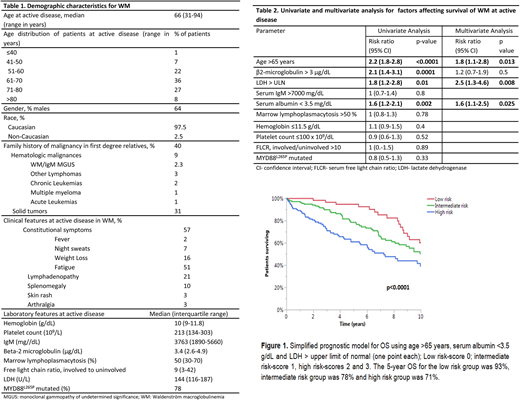
Results: We identified 889 patients with active WM. The median follow up was 8.2 years (95% CI: 7.5-9 years). The baseline characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. At the time of diagnosis of WM, 16% of patients had previously documented MGUS and 16% patients had smoldering (asymptomatic) WM. The course of WM was complicated by systemic amyloidosis in 8% (n=69), transformation to high-grade lymphoma in 4% (n=38), symptomatic hyperviscosity in 13% (n=118), myelodysplastic syndrome in 2% (n=17) and Bing-Neel syndrome in 1.4% (n=12) of patients. Of the patients tested, cryoglobulinemia was present in 17% (n=48), cold agglutinin disease in 34% (n=43) and Coombs positive hemolytic anemia in 9% (n=34) patients. The median OS was 10.6 years (95% CI: 9.7-11.4 years). The factors affecting OS are shown in Table 2. While the patients' MYD88L265P mutation status was not found to be prognostic for OS, age >65 years [RR 1.8 (95% CI: 1.2-2.8); p=0.01], LDH > upper limit of normal [RR 2.5 (95% CI: 1.3-4.6); p=0.003] and serum albumin <3.5 g/dL [RR 1.6 (95% CI: 1.1-2.5); p=0.02] were independently prognostic.
Owing to comparable RRs, each of these were assigned a score of 1 point and a prognostic model with a minimum score of 0 and maximum score of 3 was constructed. A score of 0 was considered as low risk WM and 1 as intermediate risk WM. The patients with scores of 2 and 3 were analyzed together to form the high risk cohort due to comparable OS for these two groups. The patient outcomes based on this prognostic model are depicted in Figure 1. Using the new prognostic model (n-=341), the median OS for the low risk group (n=71, 21%) was 14.6 years (95% CI: 9 years- not reached) compared to 11 years (95% CI: 8.1-14.7 years) for intermediate risk (n=140, 41% ) and 7.2 years (95 % CI: 5.4-10 years) for the high risk group (n=130, 38%), p<0.0001. The data for the IPSS-WM were available in 319 patients in the entire cohort. The OS for low risk IPSS (n=56) was 14.6 years (95% CI: 12.1 years-NR), 15.6 years (95% CI: 8.3-18.5 years) for intermediate risk IPSS (n=131) and 9.1 years (95% CI: 6.8-11.2 yeas) for the high risk IPSS group (n=132; p=0.009). Among the 220 patients having data for IPSS-WM as well as our proposed model, the current three variable model held its prognostic significance (p=0.0004). The Harrell's c-index was 0.647 (95% CI 0.592-0.702) for our prognostic model and 0.58 (95%CI: 0.521-0.638) for IPSS-WM.
Common frontline treatment comprised of rituximab monotherapy (n=277, 33%), rituximab with alkylator or purine analog combination (n=255, 30.5%) and other therapies, including alkylators/purine analog monotherapy, ibrutinib, proteasome inhibitors, etc., in 37% patients.
Conclusion: A simpler, clinically useful, risk stratification model based on age, serum albumin and serum LDH with a potentially higher discriminatory value than IPSS-WM may be used to prognosticate patients with WM. This model requires external validation.
Ansell:Pfizer: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Celldex: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Trillium: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; LAM Therapeutics: Research Funding; Merck & Co: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding. Dispenzieri:Celgene, Takeda, Prothena, Jannsen, Pfizer, Alnylam, GSK: Research Funding. Gertz:Abbvie: Consultancy; Prothena: Honoraria; Medscape: Consultancy; annexon: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Alnylam: Honoraria; Teva: Consultancy; janssen: Consultancy; Physicians Education Resource: Consultancy; Ionis: Honoraria; spectrum: Consultancy, Honoraria; celgene: Consultancy; Research to Practice: Consultancy; Apellis: Consultancy. Witzig:Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Lacy:Celgene: Research Funding. Dingli:Millennium Takeda: Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Participates in the International PNH Registry (for Mayo Clinic, Rochester) for Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Participates in the International PNH Registry (for Mayo Clinic, Rochester) for Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Millennium Takeda: Research Funding. Kumar:Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Research Funding; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Kapoor:Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal